
The Enhanced Eclipse® Model 705 is a 24 VDC loop-powered transmitter based upon the revolutionary guided wave radar (GWR) technology. This single transmitter can be used with all probe types and offers enhanced reliability, as demonstrated by a Safe Failure Fraction of 91%.
The ECLIPSE guided wave radar transmitter is designed to provide measurement performance well beyond that of many traditional technologies. The innovative, patented enclosure is a first in the industry orienting both wiring and electronics compartments in the same plane; and, angled to maximize ease of wiring, configuration and data display.

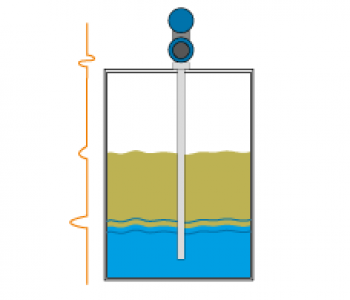
 Guided Wave Radar Probes
Guided Wave Radar Probes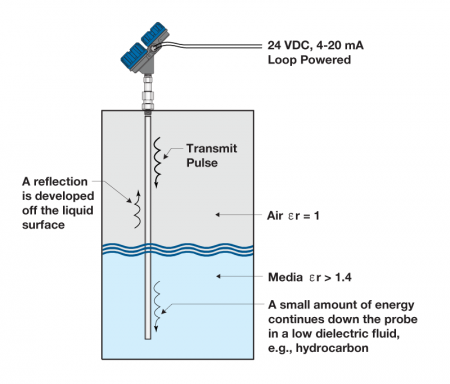 Ultrasonic pulses are emitted from the transducer, and the time required for the echo to reflect from the liquid surface and return to the transducer is measured.
Ultrasonic pulses are emitted from the transducer, and the time required for the echo to reflect from the liquid surface and return to the transducer is measured.